Heavy rainfall fills Spain’s reservoirs — and brings flash flooding
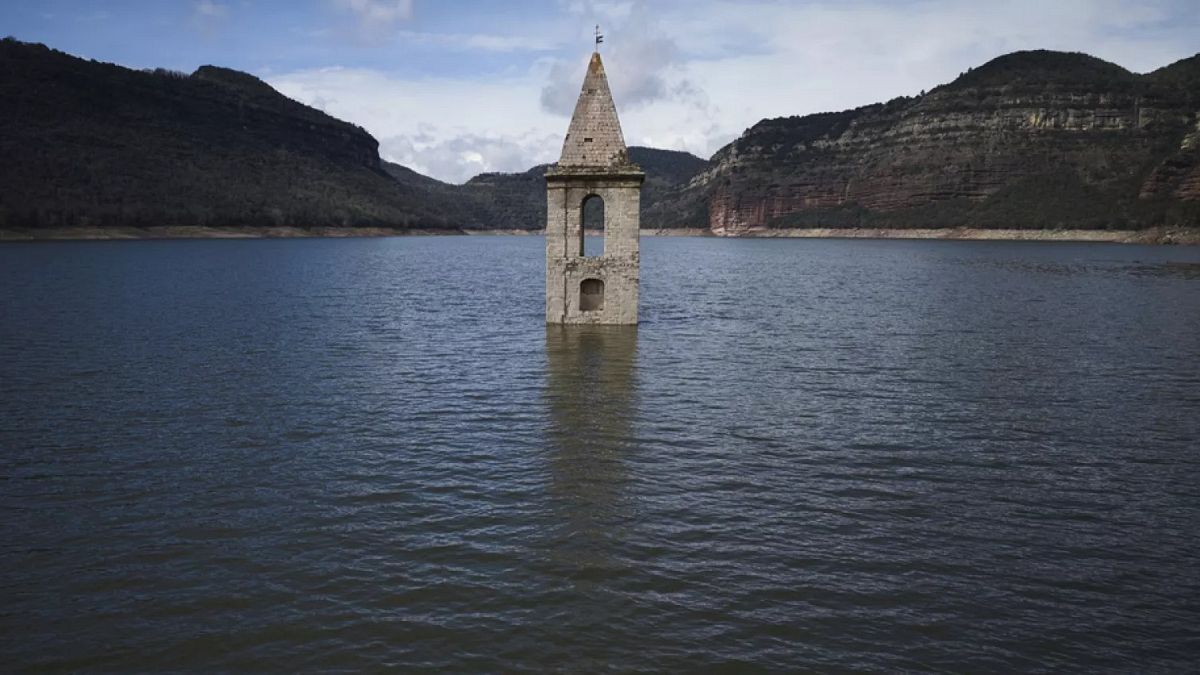

Reservoirs around the country are now around 66% full on average, according to Spain’s environment and ecological transition ministry — the highest level in a decade.
Drought relief in Spain has come at a price as flash floods and record rainfall forces hundreds to evacuate their homes, closes schools and sweeps cars away.
Parts of the country suffered from a stubborn drought last year, but the weather has recently taken an abrupt turn.
In the first 18 days of March, Spain received more than double the normal amount of monthly rainfall, according to Spanish national weather agency, AEMET.
That included normally arid regions like Andalusia, where flooded rivers forced hundreds of people to evacuate.
Madrid had more rainfall in the first three weeks of this month than any month since records began in 1893, said an AEMET meteorologist.
But volatile weather is a fact of life in Spain.
“The blessing and curse of the Spanish climate is exactly that,” said Daniel Argüeso, a climate scientist at Spain’s University of the Balearic Islands.
“We have these periods of extended drought that usually end with these kinds of situations. Having said that, the rain we had in March has been quite exceptional.”
For now, a drought that began in 2023 is over. The Sau reservoir that supplies water to Barcelona is now about 48% full, compared to less than 5% at the same time last year.
How long Spanish water reserves remain at healthy levels will depend on factors like how much more springtime rain the country gets and the heat and dryness of the summer to come.
However, climate scientists believe Spain will likely stay free of water restrictions at least through the summer.
The recent floods took place only months after a deadly deluge in Valencia killed hundreds after some areas saw a year’s worth of rain in just eight hours.
Scientists say climate change is making swings between dryness and downpour more acute.
Around the world, rising temperatures are speeding up the hydrological cycle in which water moves between the Earth and its atmosphere. That triggers extreme weather like prolonged droughts and intense rainfall.
Source: Euro News