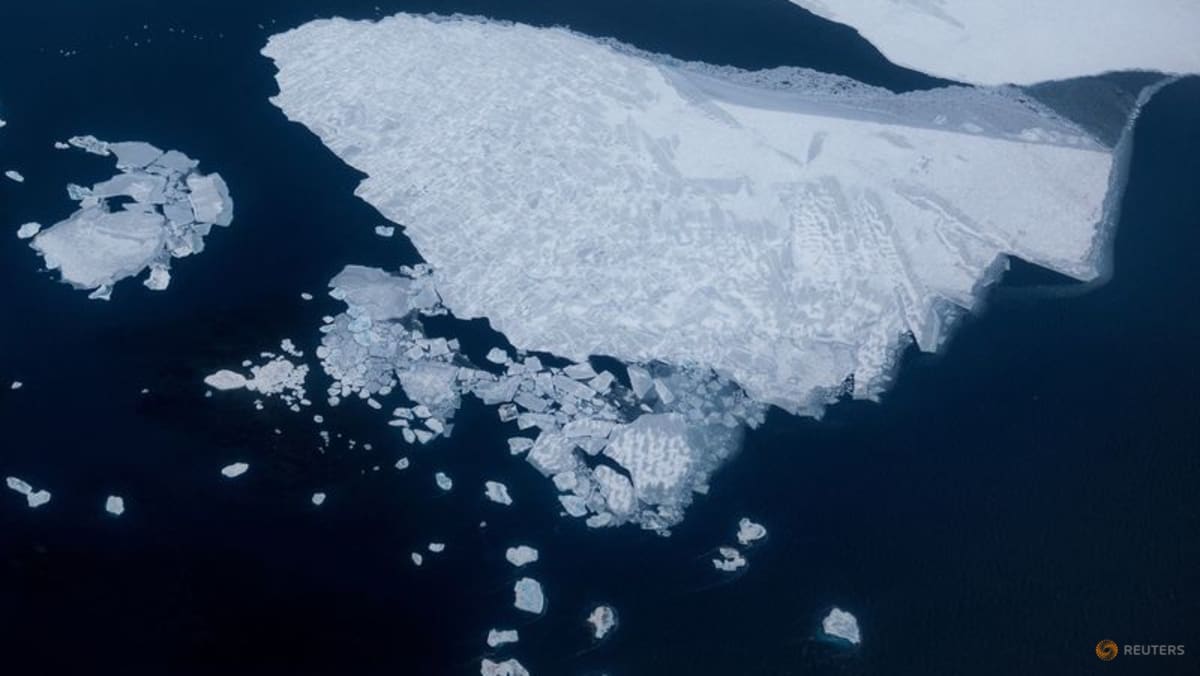
Himalayan glaciers on track to lose up to 75% of ice by 2100: Report

Further advances in satellite technology in the past five years, alongside bolstered field efforts, have buoyed scientists’ understanding of the changes underway. The report draws on data running through December 2022.
“While the knowledge of the Himalayan glaciers is still not as good as the Alps, it’s now comparable to other regions like the Andes,” said Tobias Bolch, a glaciologist with Graz University of Technology in Austria unaffiliated with the report.
Compared with a 2019 ICIMOD assessment of the region, “there’s a much higher level of confidence now in these findings”, said Wester. “We have a better sense of what the loss will be through to 2100 at different levels of global warming.”
LIVELIHOODS AT RISK
With this newfound understanding comes grave concern for the people living in the Hindu Kush Himalaya.
The report found water flows in the region’s 12 river basins, including the Ganges, Indus, and Mekong, are likely to peak around mid-century, with consequences for the more than 1.6 billion people who depend on this supply.
“While it may sound like we’ll have more water because glaciers are melting at an increased rate … too frequently it will arise as floods instead of a steady flow,” said Wester. Past peak water, supplies will eventually dwindle.
Many high mountain communities use glacial water and snowmelt to irrigate crops. But the timing of when snow falls has become more erratic, and there is less than there used to be.
“We’ve had … huge numbers of yak deaths because during summer they go to higher pastures,” said report co-author Amina Maharjan, a senior specialist in livelihoods and migration at ICIMOD. If the snow falls too soon, “the entire area is covered in snow and they don’t have grass to graze”.
People are now moving away from mountain communities to earn income elsewhere, she said.
Melting glaciers also pose a danger to downstream communities. Runoff pools in shallow lakes, held back by rocks and debris. The risk comes when a lake overfills, bursting through its natural barrier and sending a torrent of water rushing down mountain valleys.
Governments are trying to prepare for these changes. China is working to shore up the country’s water supplies. And Pakistan is installing early warning systems for glacial lake outburst floods.
Source: CNA