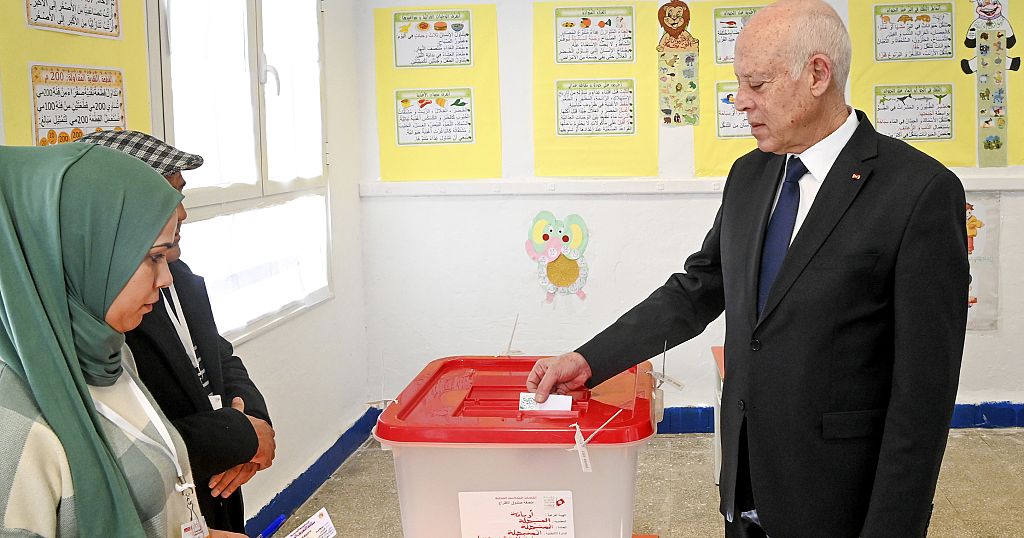
Tunisians vote in local elections on Sunday to fill a new chamber

Butter and milk shortages. Political party boycotts. Ongoing prosecutions of the president’s critics.
This is the environment in which Tunisians will head to the polls on Sunday for the country’s first local elections since President Kais Saied wrote a new constitution that voters approved last year.
Voting will determine the composition of a new National Council of Regions and Districts — one component of Saied’s vision to reshape politics in Tunisia, the country that sparked the region-wide uprisings that became known as the Arab Spring 12 years ago.
The new legislative chamber is designed to focus on economic development and candidates have campaigned on the radio about building schools, roads and other infrastructure. It harkens back to Saied’s campaign promise to distribute power and funds far from Tunisia’s capital. Tunis is synonymous with widely criticized government bureaucracy whose unpopularity helped fuel Saied’s rise.
But despite the transformation promised, few signs of enthusiasm about elections and their ability to buoy Tunisia are apparent. In the 13th election since the 2011 revolution, there’s little understanding about the stakes, what the new chamber has the power to do and whether voting even matters.
“People used to be motivated in other elections but nobody talks about this one or is up to date,” said Najib, a cafe owner in La Goulette who said in past contests candidates regularly put up signs throughout his establishment. He declined to give his name out of fear of losing customers.
Such is a familiar story for Tunisia, a country plagued by high unemployment, drought and shortages of basic necessities that credit ratings firms say is teetering on the verge of bankruptcy.
Amid a similar lack of enthusiasm, barely 11% of voters turned out for parliamentary elections last year even with growing concerns about the country’s political and economic woes.
Tunisia recently passed a new budget without major reforms that could bolster the economy or lure foreign lenders. It retains price controls and subsidies for flour, electricity and fuel. That’s even though reducing government spending on subsidies is one reform that the IMF has demanded in exchange for a $1.9 billion loan.
“The government is not living up to its responsibilities with regard to subsidies, which explains the scarcity of products,” said Aram Belhadj, a professor at the School of Economy and Management of Tunis.
Though the subsidies are written into the budget, Tunisia’s recent pattern of not compensating vendors has exacerbated shortages for goods like baguettes, he added. Despite political apathy, he noted that amid the shortages, people had begun paying closer attention to budgetary matters.
Without reforms, the ratings firm Fitch this month affirmed its assessment that Tunisia was at high risk for default with a CCC- rating, noting it did “not expect reforms will progress in 2024, in the context of the presidential election.”
The problems are apparent but there’s little recognition among the electorate that elections are taking place. They come more than two years after Saied suspended the country’s parliament and months after he dissolved municipal councils, further dismantling the systems put in place after the 2011 revolution.
That decision added to the outrage that Saied’s opponents have voiced since July 25, 2021, when he consolidated power, froze the parliament and sacked the prime minister. He has since imprisoned dozens of critics from business and political spheres, including Rached Ghannouchi, the leader of the political party Ennahda that ascended to power after last decade’s revolution.
Ennahda is among those who won’t participate in the elections. The party is part of the National Salvation Front coalition that is boycotting along with others including Tunisia’s Workers’ Party and the Free Destourian Party, whose leader Abir Moussi was imprisoned Oct. 3 for allegedly undermining state security.
“The political and social climate is not conducive to holding this local election, which does not meet international standards of democracy,” Ahmed Chebbi, the head of a leading coalition of opposition parties said at a news conference in November.
Apart from the boycotts, Fadil Alireza, a non-resident scholar at the Middle East Institute, said Tunisians had gradually become disillusioned about elections leading to better standards of living.
“People run. They make promises of what they’ll do and that Tunisia will be better. The fact that we’ve seen consistent decreasing purchasing power and deteriorating services — health, education, transportation … makes disillusionment set in,” he said.
ISIE, Tunisia’s Independent High Authority for Elections, is sending out frequent text messages to remind voters about the election. Mohamed Tlili Mnasri, the authority’s spokesperson, said there had been few notable irregularities and that the authority was working to educate voters on the legislative chamber up for election.
He acknowledged expectations for low voter turnout and boycotts. But he said there were no thresholds for voting for the new chamber to be elected. And for democracies, what’s important is making the opportunity to vote available, he said.
“We’re still in the process of stabilizing institutions,” Mnasri said. “That’s what democratic transition is.”
Source: Africanews